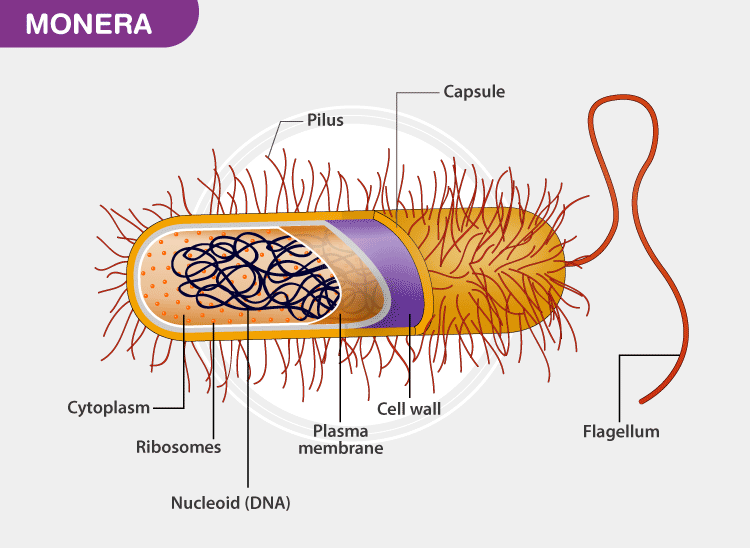
Kingdom Monera belongs to the prokaryote family. The organisms belonging to this kingdom do not contain a true nucleus. These are the oldest known microorganisms on earth. Their DNA is not enclosed within the nucleus.
They are unicellular organism found mostly in a moist environment. They are found in hot springs, snow, deep oceans or as parasites in other organisms.
The monerans do not possess any membrane-bound organelles.
Let us go through the kingdom monera notes to explore the characteristics and classification of monera.
Characteristics of Monera
The important characteristics of Monera are mentioned below:
- The Monerans are unicellular organisms.
- They contain 70S ribosomes.
- The DNA is naked and is not bound by a nuclear membrane.
- It lacks organelles like mitochondria, lysosomes, plastids, Golgi bodies, endoplasmic reticulum, centrosome, etc.
- They reproduce asexually by binary fission or budding.
- The cell wall is rigid and made up of peptidoglycan.
- Flagella serves as the locomotory organ.
- These are environmental decomposers and mineralizers.
- They show different modes of nutrition such as autotrophic, parasitic, heterotrophic, or saprophytic.
Bacteria
Bacteria are microscopic organisms that can survive in diverse environments. They can be beneficial as well as harmful. They possess a simple structure without a nucleus and a few cell organelles.
The bacteria are surrounded by two protective coverings- the outer cell wall and the inner cell membrane. Some bacteria are also covered by a capsule. Few bacteria like Mycoplasma do not have a cell wall.
Short whip-like extensions known as pili surround the surface of the bacteria. The long whip-like structures are known as flagella.
They exhibit autotrophic and heterotrophic modes of nutrition. Autotrophic bacteria derive nutrition from inorganic substances. They derive carbon and hydrogen from atmospheric carbon dioxide, H2, H2S, and NH3. The heterotrophic bacteria depend upon external organic materials for their food. These can be saprotrophs, parasites, and symbionts.
Bacterial Shape
Bacteria possess the following different shapes:
Cocci- Bacteria are spherical or oval in shape. These can be micrococcus (single), diplococcus (in pairs), tetracoccus (in fours), streptococcus (in chains), and staphylococcus (in clusters like grapes)
Bacilli- These are rod-shaped bacteria with or without flagella.
Vibrios- These are comma or kidney-shaped small bacteria with flagella at one end.
Spirillum- These are spiral or coiled shaped. They are rigid forms due to the spiral structure and bear flagella at one or both the ends.
Filament- The body consists of small filaments like fungal mycelia.
Stalked- The bacterium possesses a stalk.
Budded– The body of the bacterium is swollen at places.
Classification of Monera
Kingdom Monera is classified into three sub-kingdoms- Archaebacteria, Eubacteria, and Cyanobacteria.
Archaebacteria
- These are the most ancient bacteria found in the most extreme habitats such as salty area (halophiles), hot springs (thermoacidophiles), and marshy areas (methanogens).
- The structure of the cell wall is different from that of the other bacteria which helps them survive in extreme conditions.
- The mode of nutrition is autotrophic.
- The nucleotide sequences of its t-RNA and r-RNA are unique.
Eubacteria
- Eubacteria are also known as “true bacteria”.
- The cell wall is rigid and made up of peptidoglycans.
- It moves with the help of flagella.
- A few bacteria contain short appendages on the cell surface known as pili which help the bacteria during sexual reproduction. Pili also helps a pathogen to attach to the host.
- They are divided into two categories; gram positive and gram negative, depending upon the nature of the cell wall and the stain they take.
- Rhizobium and Clostridium are two eubacteria.
Cyanobacteria
- These are also known as blue-green algae.
- These bacteria are photosynthetic in nature.
- They contain chlorophyll, carotenoids, and phycobilins.
- They are found in the aquatic region.
- Some of these even fix atmospheric nitrogen.
- Nostoc, Anabaena, Spirulina are some of the cyanobacteria.
Monerans are very useful organisms. They enrich the soil and serve as an important part of the nitrogen cycle. They are also helpful in the production of some food items, and antibiotics. Methanogens play an important role in the treatment of sewage. Many organisms rely on archaebacteria as the source of food.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are Monerans?
Monerans are unicellular, prokaryotic organisms found in a moist environment and lack a true nucleus.
How does Monera feed?
Monera breakdown the dead matter and food in our digestive system. They can also prepare their own food but bacteria feed on dead matter.
Where is Monera found?
Monera is found in the moist environment. They can be found in hot springs deep oceans, snow and as parasites in organisms.
How are Monerans classified?
Monerans are classified into three phyla:
- Archaebacteria
- Eubacteria
- Cyanobacteria
How does Monera reproduce?
Monera reproduces by asexually by binary fission during favourable conditions or endospore formation during unfavourable conditions. They reproduce sexually by a process called conjugation
No comments:
Post a Comment